SZJ Returns to The Battery Show Europe, Showcasing Turnkey Lithium Battery Intelligent Manufacturing Solutions
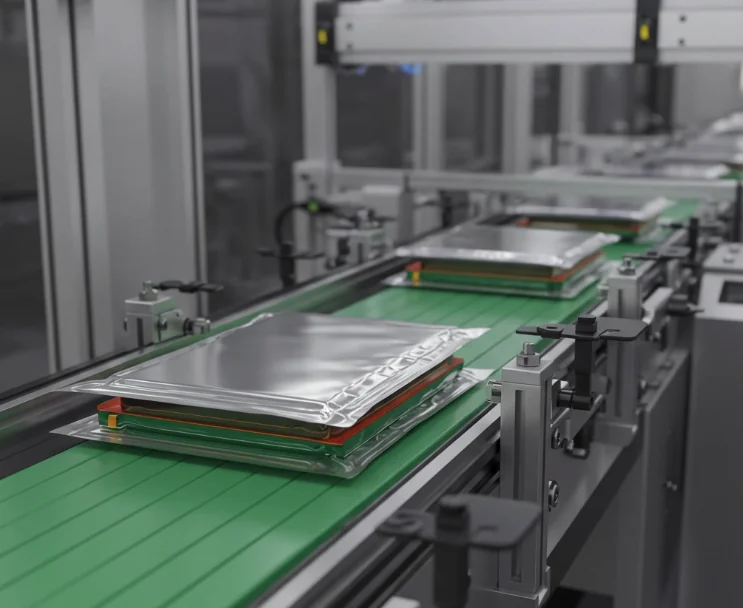
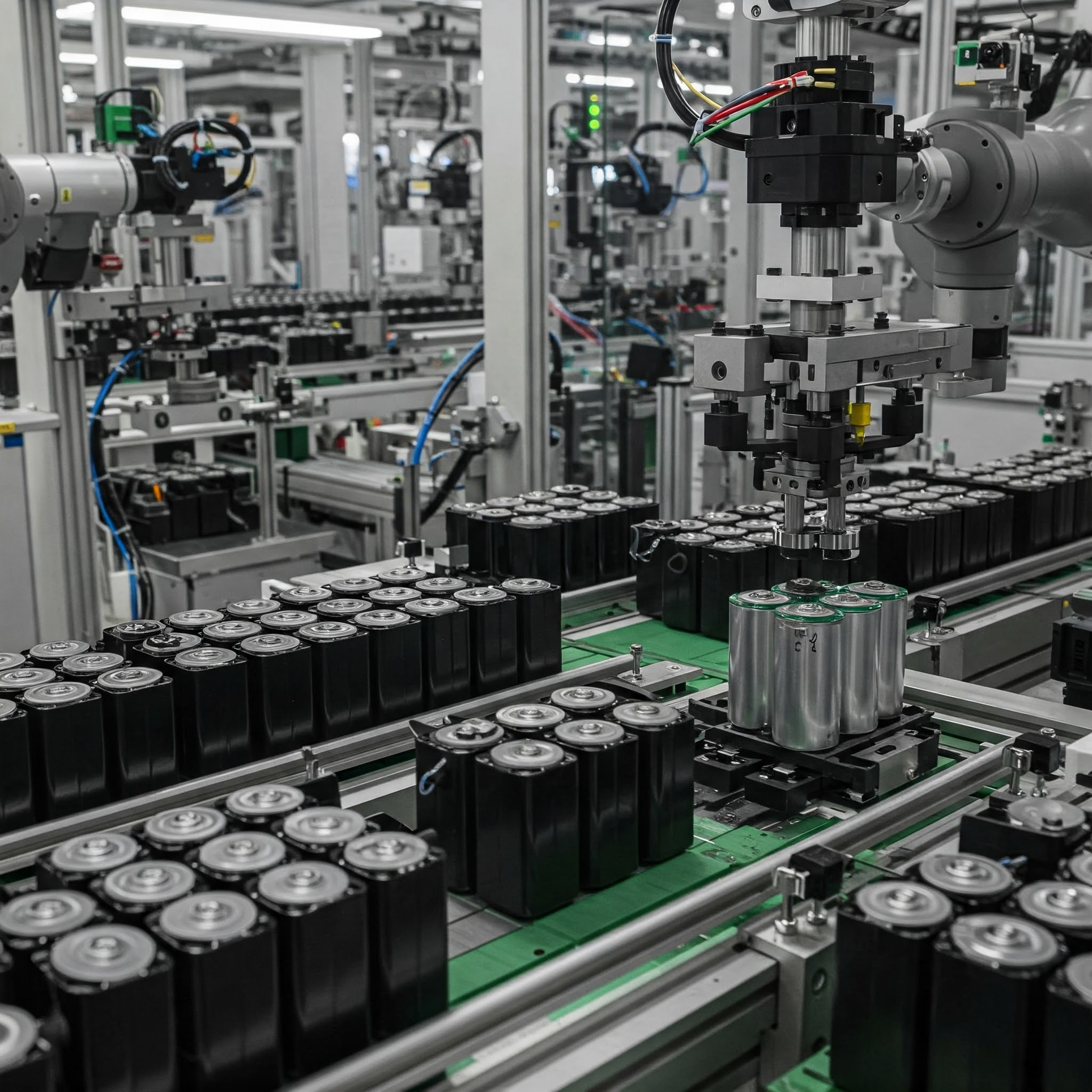
From June 3 to 5, 2025, SZJ once again made its presence felt at The Battery Show Europe in Stuttgart, Germany, marking its second consecutive participation in this premier global event for the battery industry. As a leading company focused on intelligent manufacturing solutions for lithium battery equipment, SZJ is accelerating its pace of technological innovation and international market expansion. By offering more targeted, end-to-end production line solutions, the company is deepening collaboration and communication with clients worldwide. At the exhibition, SZJ presented its aluminum shell battery intelligent manufacturing line model. This solution reflects the company’s systematic approach to automation coordination, process alignment, and production line layout. It attracted widespread interest, with many visitors engaging in discussions on efficiency optimization, module compatibility, and flexible design strategies. In the cylindrical cell sector, SZJ showcased its dual-technology solution combining grooving and laser sealing. The production line integrates high-speed transfer systems, precision forming, and fully automated welding modules. It delivers a single-line capacity of up to 350 PPM with a product yield rate exceeding 99.5%, offering strong support for the efficient and stable mass production of large cylindrical cells. This demonstrated SZJ’s robust system integration capabilities for high-throughput applications. During the exhibition, SZJ’s business team engaged in face-to-face meetings with clients from various countries and regions. These conversations highlighted the company’s integrated approach to matching battery structures with tailored production processes. Through on-site demonstrations and technical briefings, clients gained deeper insights into SZJ’s engineering strengths in system-level design. Looking ahead, SZJ will remain customer-centric, focusing on key process technologies and continuously refining its integration capabilities. The company is committed to advancing the global adoption of intelligent manufacturing solutions across the battery industry.